A comprehensive guide to Skin tightening
At Albany Cosmetic and Laser Centre in Edmonton, we offer a variety of skin-tightening options to help you achieve smoother, firmer, and more youthful-looking skin.
- Our advanced laser treatments employ the latest technologies to target areas of loose or sagging skin on the face and body. Depending on your individual needs, our treatments can be tailored to target the specific areas that you wish to address.
- Our experienced practitioners will assess your unique facial anatomy and discuss with you the best treatment for achieving optimal results. Our clinic also offers non-invasive solutions for those who want a less invasive approach to skin tightening.
- These treatments usually employ light energy sources such as radio frequency or ultrasound technology, which work by stimulating collagen production resulting in firmer skin with improved texture and tone.
- Many people opt for these treatments because they are virtually painless with minimal downtime needed afterwards – in fact, most patients can return to their normal activities right away!
Skin Tightening Results
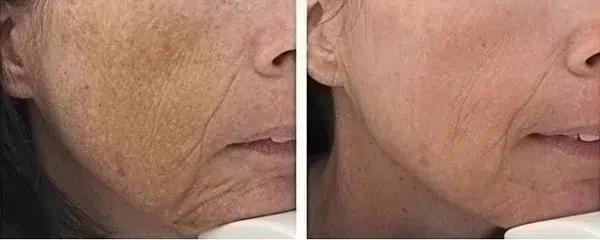
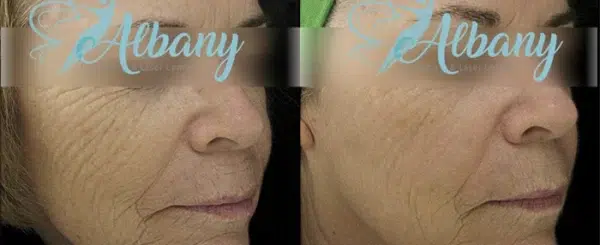
The results of a skin tightening treatment will vary depending on the type of procedure, the health and age of the patient’s skin, and how it is administered. Generally speaking, patients can expect to see some improvement in their complexion with single treatments but may need multiple treatments for longer-lasting effects. Commonly reported improvements include smoother-looking skin, tighter pores, diminished wrinkles and fine lines, improved firmness and elasticity, and improved overall texture. Patients with more pronounced signs of aging may need to combine skin-tightening treatments with other therapies such as facial fillers or laser resurfacing in order to achieve their desired results. Additionally, many experts believe that maintaining regular skincare routines such as cleansing, exfoliating, moisturizing and protecting the skin from further damage are key components to sustaining longer-term results from any type of skin tightening treatment.

Skin tightening options At Albany Laser
Our clinic also offers non-invasive solutions for those who want a less invasive approach to skin tightening. These treatments usually employ light energy sources such as radio frequency or ultrasound technology which work by stimulating collagen production resulting in firmer skin with improved texture and tone. Many people opt for these treatments because they are virtually painless with minimal downtime needed afterwards – in fact, most patients can return to their normal activities right away!
- Deep Laser treatment: Several laser therapy treatments can aid in collagen formation and overall skin tone improvement. The majority of people have the best outcomes after numerous treatments. Laser therapy can help firm the upper arms and stomach, among other body parts.
- Skin Resurfacing: Laser resurfacing removes the top layers of skin while sending heat deep into the layers underneath. Laser peeling is another term for it.
- Focused Ultrasound (HIFU). This treatment uses heat to penetrate deep into the skin’s layers, promoting collagen formation and lifting sagging skin. It may take many months before you see an improvement in the firmness and suppleness of your skin. Ultrasound findings are not permanent and generally last approximately a year.
- Microneedling: At Albany Cosmetic and Laser Centre, we specialize in providing skin tightening treatments with Botox, fillers and threads.
- Botox is a popular injection for reducing the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and other signs of aging.
- For more dramatic results, dermal fillers can be injected into the skin to plump up sagging areas like the cheeks and temples.
- Threads offer a non-invasive option that involves inserting specialized threading under the skin to instantly lift and tighten without needles or surgery.
The benefits of these treatments include an increase in elasticity leading to smoother, firmer skin; improved texture and tone; reduced wrinkles; better hydration; and an overall youthful-looking complexion. Our experienced team will customize treatment plans according to your individual needs for optimal results with minimal downtime. Whether you’re looking to reduce wrinkles or sagging skin, our experienced professionals will make sure you get the best outcome possible from your treatments at Albany Cosmetic and Laser Centre.
