Melasma Treatment in Edmonton: Reveal Radiant Skin
Melasma is a stubborn pigmentation condition that often appears as brown or greyish patches, typically on the cheeks, forehead, or upper lip. It’s commonly triggered by sun exposure, hormones, or genetics. At Albany Cosmetic and Laser Centre in Edmonton, we offer a cutting-edge melasma protocol that combines pharmaceutical-grade creams, precision injections, and advanced skin treatments to restore clarity and glow.
Our proprietary treatment plan is customized for each patient and includes a multi-step approach that prepares your skin, treats the pigmentation at the source, and supports long-lasting results. With the right care and expert guidance, achieving even-toned, radiant skin is well within reach
Treatment cost

Understanding Melasma, the mask of pregnancy
Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by dark, irregularly shaped patches on the face, particularly on the forehead, cheeks, and upper lip. It is caused by an overproduction of melanin, the pigment that gives color to our skin, hair, and eyes.
- The exact pathology of Melasma is still not fully understood, but it is believed to be caused by a combination of factors including hormonal changes, sun exposure, genetics, and certain medications.
- Risk factors for Melasma include being female, having darker skin, being pregnant, using hormonal contraceptives, and being exposed to UV radiation from the sun. Women with a family history of Melasma, or who have experienced hormonal changes, such as pregnancy or menopause, are also more likely to develop the condition.
- Individuals with skin type 4, particularly those of Middle Eastern, Asian, and Indian descent, are more susceptible to Melasma due to the high levels of melanin in their skin. Melanin is the pigment that gives color to the skin, hair, and eyes, and it provides some protection from the sun’s harmful rays. However, in individuals with high levels of melanin, the skin is more likely to overproduce melanin in response to sun exposure, hormonal changes, or other triggers, leading to the development of dark patches known as Melasma. It is also important to note that genetics play a role in the development of Melasma, so if you have a family history of the condition, you may be at higher risk.
It’s important for patients to understand that Melasma is not just a cosmetic issue, but a complex medical condition that can have a significant impact on their self-esteem and quality of life. At Albany Cosmetic and Laser Centre, our goal is to help our patients understand the causes and risk factors of Melasma and to provide them with the most effective and advanced treatment options available to achieve clear, radiant skin.
Melasma Tretament options
At Albany Cosmetic and Laser Centre, we offer a range of advanced Melasma treatments to meet the unique needs of each patient, including:
- Fraxel Laser is non-invasive laser treatment uses fractional laser technology to target the deeper layers of the skin, stimulating the production of collagen and reducing the appearance of Melasma. Benefits of Fraxel laser include reduced pigmentation, improved skin texture, and a more youthful and radiant complexion.
- Microneedling with PRP combines microneedling with Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP), which is derived from the patient’s own blood. The microneedling procedure creates micro-injuries in the skin, promoting healing and rejuvenation, while the PRP helps to improve the skin’s overall appearance and reduce the appearance of Melasma.
- Hydrafacial is an advanced skincare treatment uses a combination of cleansing, exfoliation, hydration, and nourishment to improve the overall health and appearance of the skin. It can be effective in reducing the appearance of Melasma, as well as improving skin texture and tone.
- Tranexamic Acid Meso Injections: This treatment uses a combination of tranexamic acid and hyaluronic acid to help reduce the appearance of Melasma and improve the overall health of the skin. The injections are performed by a qualified medical practitioner and are relatively quick and easy, with minimal downtime.
- Chemical Peels uses a solution to exfoliate the top layers of skin, revealing fresher, smoother, and more even-toned skin underneath. They can be effective in reducing the appearance of Melasma, as well as improving skin texture, tone, and fine lines and wrinkles.
- CO2 Fractional Laser uses advanced technology to target superficial and deep layers of the skin, reducing the appearance of Melasma and improving the overall health and appearance of the skin. It is a safe and effective treatment option, with little to no downtime required.
While these treatments can be highly effective in reducing the appearance of Melasma, it’s important to note that there may be potential side effects, including redness, swelling, itching, and peeling. These side effects are generally mild and short-lived, and our team of experts will work with you to minimize any discomfort and ensure a safe and effective treatment experience.
Stunning Melasma Treatment Results You Can See
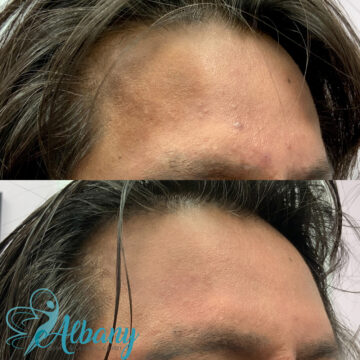
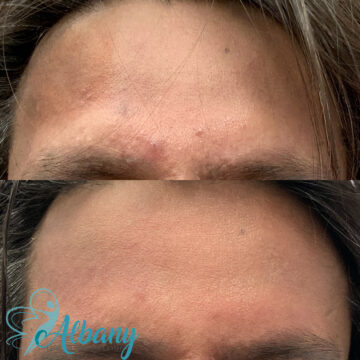

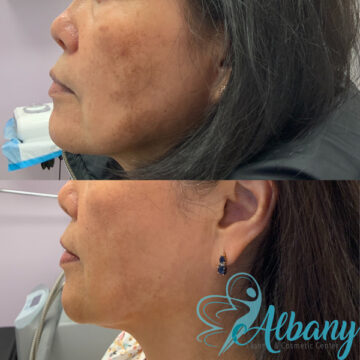
Patients often notice a visible reduction in pigmentation and improved skin texture within a few sessions. Depending on the treatment plan, results can include lighter patches, even skin tone, and a brighter complexion.
Prep and Aftercare Timeline for Melasma Treatment
Start applying the prescribed compounded lightening cream daily as directed.
Avoid excessive sun exposure, tanning beds, and harsh skincare products.
Treatment Day: Before Appointment
Discontinue the lightening cream 3 days before your scheduled session.
Arrive with clean, makeup-free skin and avoid applying any lotions or creams that day.
1–7 Days After: Initial Healing
Resume the lightening cream according to the treatment type:
24 hours after HydraFacial or microneedling
3 days after Fraxel laser
7 days after CO2 laser
Use only gentle cleansers and hydrating moisturizers during this period.
Apply a broad-spectrum SPF 50+ sunscreen daily, even indoors or on cloudy days.
7–14 Days After: Recovery
Continue using the brightening cream and sun protection as directed.
Reintroduce regular skincare products gradually, avoiding retinoids and exfoliants.
3–6 Months After: Maintenance
Repeat the melasma protocol cycle as advised to maintain and enhance results.
Stick to a maintenance routine with pigment-suppressing skincare and sun protection.