Hair Follicle: Understanding Its Structure and Function
Hair follicles are complex, tiny structures located within the skin responsible for producing and growing hair. Understanding how hair follicles work and what makes them vulnerable to damage is crucial for anyone seeking effective hair reduction treatments at Albany Cosmetic and Laser Centre.
This page will guide you through the anatomy of hair follicles, their growth phases, and how modern technologies precisely target them to achieve long-lasting results.
What Is A Hair Follicle?
A hair follicle is a tiny but intricate structure within the skin that anchors the hair into place. Located in the dermis, each follicle contains a hair bulb, where living cells divide to form the hair shaft. The follicle also contains sebaceous glands, blood vessels, and nerves that support hair growth and nourishment.
The melanin present within the hair bulb plays a critical role when targeting follicles for hair reduction, as it absorbs specific light wavelengths during treatment, making the follicle vulnerable to heat damage.
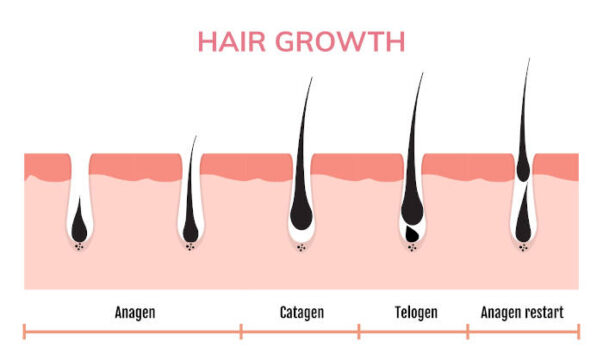
The Hair Growth Cycle
Hair follicles go through a natural cycle consisting of three main phases:
- Anagen (Growth Phase): During this phase, the hair follicle is actively producing hair. This is the phase where the follicle is most susceptible to external influences aimed at disrupting hair growth.
- Catagen (Transitional Phase): A short phase where hair growth stops, and the hair follicle begins to shrink. During this phase, treatments targeting hair follicles are less effective.
- Telogen (Resting Phase): The follicle remains dormant, and the hair eventually sheds. New hair begins to grow from the same follicle as it re-enters the Anagen phase.
Why Targeting The Anagen Phase Matters
The Anagen phase is the most critical stage for effective laser hair reduction because the hair is actively growing and is well-connected to the follicle’s root. Techniques designed to disrupt hair growth are most successful when the follicle is in this stage. As hair follicles do not all enter this phase simultaneously, multiple sessions are necessary to achieve desired results.
Hair Follicle Structure Explained
Each hair follicle is made up of several essential parts:
- Hair Bulb: The rounded base of the follicle where hair cells divide and grow. This area contains high concentrations of melanin, making it an ideal target for hair reduction methods.
- Dermal Papilla: A structure at the base of the hair bulb providing blood supply and essential nutrients to support hair growth.
- Outer Root Sheath: A protective layer surrounding the follicle, ensuring proper guidance and support for developing hair.
- Inner Root Sheath: A delicate layer that helps form the hair shaft and guide it towards the surface of the skin.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hair Follicles
What Is The Role Of The Hair Follicle In Hair Growth?
Hair follicles are the foundation of hair growth. They produce and nourish hair through cellular division within the hair bulb, supported by nutrients from the dermal papilla.
Why Are Hair Follicles Targeted During Treatment?
Hair follicles are targeted because disrupting their function during the growth phase can significantly reduce their ability to regrow hair over time.
How Does Hair Color Affect Follicle Treatment?
Melanin within the follicle determines how effectively certain treatments work. Darker hair with more melanin generally responds better to various methods aimed at disrupting follicle growth.
Can Hair Follicles Regenerate After Treatment?
Some hair follicles may partially recover over time, but their ability to produce hair is usually reduced. Maintenance sessions may be needed for long-term results.
What Makes The Anagen Phase Most Effective For Hair Reduction?
During the Anagen phase, the hair follicle is actively producing hair and is rich in melanin, making it highly responsive to external treatments aimed at halting hair growth.
How Can I Enhance The Results Of My Treatments?
Following pre-treatment and aftercare guidelines from Albany Cosmetic and Laser Centre will ensure your hair follicles are effectively targeted for the best possible outcome.
