Mechanism of Action in Edmonton
Curious what Botox® actually does after it’s injected—and why technique and dosing matter so much? At Albany Cosmetic & Laser Centre in Edmonton, we use precision neuromodulator injections (Botox®, Dysport®, Xeomin®, Nuceiva®) to temporarily relax specific muscles that create dynamic wrinkles like forehead lines, frown lines (11s), and crow’s feet. If your goal is a natural, refreshed look (not a “frozen” face), request a consultation today—call, text, email, or use online chat and we’ll walk you through candidacy, timelines, and transparent pricing.
Why Understanding the Mechanism Matters
Patients who understand how neuromodulators work can make informed decisions and realistic expectations. Recognizing that the toxin does not “erase” wrinkles but temporarily relaxes specific muscles helps clients appreciate why dosage and injection technique matter. It also clarifies why consistent follow‑up treatments are necessary to maintain results.
Botox Mechanism of Action: Step-by-Step (and Why Results Wear Off)
Botox and other neuromodulators are best understood as signal blockers. They do not “fill” wrinkles and they do not change skin quality overnight. Instead, they reduce the strength of the muscle contraction that repeatedly creases the skin—so the skin has a chance to look smoother when your face is at rest and in motion.
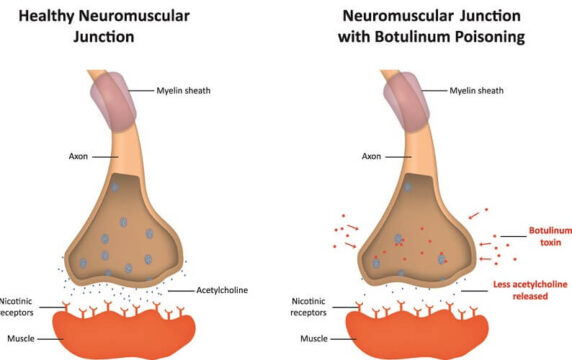
Step 1: Normal muscle contraction. Your nerve ending releases a messenger chemical called acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. That signal tells the muscle fiber to contract (for example, when you frown, squint, or raise your brows).
Step 2: Neuromodulator blocks the release signal. After injection into a targeted muscle, botulinum toxin type A is taken up by nerve terminals and disrupts the internal “release machinery” required to send acetylcholine into the junction. With less acetylcholine released, the muscle cannot contract as strongly.
Step 3: The muscle relaxes, and dynamic lines soften. As the pulling force decreases, lines created by repetitive expression (forehead creases, 11s, crow’s feet) soften gradually. Because the effect is localized and dose-dependent, a careful injector can preserve natural movement while reducing the lines you want improved.
Why it takes time: The change is biochemical, not instant. Many clients notice early improvement within several days, with a more complete result around the 10–14 day mark. This is also why follow-up timing matters for symmetry and fine-tuning.
Why results fade: The effect is temporary. Over time, the nerve terminal rebuilds functional connections and signaling returns, so muscle activity gradually comes back. Most cosmetic areas last around 3–4 months, though this varies with dose, area treated, and individual metabolism.

